eMMC¶
The MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit has an eMMC (U3) that can be used for additional storage when booting from UFS and (in the future) as a boot media itself.
Caveats¶
- Rev 1 and 2 of the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit does not have provisions to power the eMMC before the MitySOM-QC6490 is powered, which means eMMC cannot be used a boot media for these boards. Rev 3 of the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit will have this resolved.
- Rev 1 and 2 of the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit does not have a return clock connected on SDC1 interface, thus limiting the eMMC interface to HS200 speeds. Rev 3 of the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit will have this resolved.
- Rev 1 of the MitySOM-QC6490 does not have a return clock connected on SDC1, thus limiting the interface to HS200 speeds. This will be resolved in a future revision of the MitySOM-QC6490.
Development Board Configuration¶
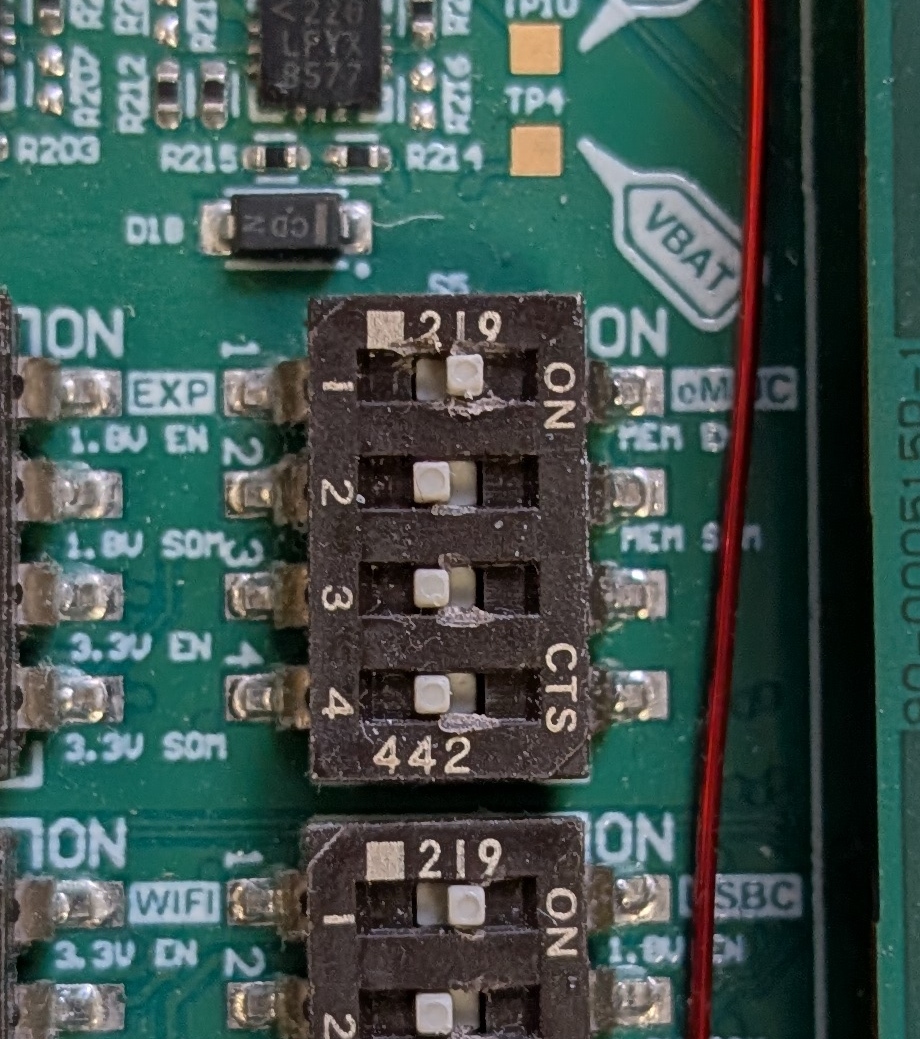
Ensure that Switch S5 is set properly.- Switch 1 should be set to enable MEM-EN, which is a top level enable to send 1.8 V to the eMMC
- Switch 2 can be either set or not set
- If Switch 2 is not set the 1.8V comes from the DC supply on the Development Kit
- If Switch 2 is set the 1.8V comes from the SOM
Usage as Additional Storage¶
Device Enumeration¶
eMMC will always appear as /dev/mmcblk0. You can use lsblk to verify the device is recognized:
root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# lsblk | grep mmcblk0 mmcblk0 179:0 0 58.3G 0 disk mmcblk0boot0 179:32 0 4M 1 disk mmcblk0boot1 179:64 0 4M 1 disk
Note that if you do not see mmcblk0, please verify the steps in Development Board Configuration were followed.
Partitioning, Formatting and Mounting¶
fdisk is recommended for partioning the eMMC.
- Run the command
fdisk /dev/mmcblk0. - Type
oand press enter. - Type
nand press enter. - Press enter.
- Press enter.
- Press enter.
- Press enter.
- The next step will commit all changes; ensure there was no remaining data on the eMMC card that you need.
- Type
wand press enter. A full transcript of the above partitioning steps should look something like the following:root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# fdisk /dev/mmcblk0 Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.39.3). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Command (m for help): o Created a new DOS (MBR) disklabel with disk identifier 0x22119e45. Command (m for help): n Partition type p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) e extended (container for logical partitions) Select (default p): Using default response p. Partition number (1-4, default 1): First sector (2048-122314751, default 2048): Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-122314751, default 122314751): Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 58.3 GiB. Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered. Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks.
lsblk can be used to verify the partition was created.
root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# lsblk | grep mmcblk0 mmcblk0 179:0 0 58.3G 0 disk `-mmcblk0p1 179:1 0 58.3G 0 part mmcblk0boot0 179:32 0 4M 1 disk mmcblk0boot1 179:64 0 4M 1 disk
Now you can make a file system on the eMMC partition you created.
We will move forward with an ext4 file system.
root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/mmcblk0p1
mke2fs 1.47.0 (5-Feb-2023)
Discarding device blocks: done
Creating filesystem with 15289088 4k blocks and 3825664 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 149deef9-6556-48c6-9d1b-a158b6d0ccf8
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (65536 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
You can now use the mount command to mount your partition:
root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# ls -l /mnt lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 21 2025 /mnt -> var/rootdirs/mnt root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# df -h Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/mmcblk0p1 57.1G 2.0M 54.2G 0% /var/rootdirs/mnt root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# mount | grep mmcblk0 /dev/mmcblk0p1 on /var/rootdirs/mnt type ext4 (rw,relatime)
Performance¶
If you want to benchmark the eMMC, fio is a highly flexible benchmarking utility that comes installed on the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit. You can read more at the link, but below is a basic fio commands (which assumes eMMC partition is mounted to /mnt) for testing read and write performance:
fio --name=emmc --filename=/mnt/emmctest --size=1G --bs=256k --iodepth=4 --numjobs=1 --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --rw=write --loops=5 --verify=crc32c
Additional Information from debugfs¶
You can get additional information on eMMC via debugfs. First, mount debugfs.
mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug/
The mmc0/ios file supplies data on the interface speed. For eMMC operating at HS200 you should expect to see the following:
root@qcs6490-mitysom-devkit:~# cat /sys/kernel/debug/mmc0/ios clock: 200000000 Hz actual clock: 192000000 Hz vdd: 18 (3.0 ~ 3.1 V) bus mode: 2 (push-pull) chip select: 0 (don't care) power mode: 2 (on) bus width: 3 (8 bits) timing spec: 9 (mmc HS200) signal voltage: 1 (1.80 V) driver type: 0 (driver type B)
Usage as Boot Media¶
Although booting the MitySOM-QC6490 from eMMC on the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit has been achieved, due to the Caveats in Rev 1 and 2 of the MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit and Rev 1 of the MitySOM-QC6490, this is not easily reproducible. First, the Rev 1 and Rev 2 MitySOM-QC6490 Development Kit needs hardware modifications to power the eMMC chip before the MitySOM-QC6490 is powered. Second, the Qualcomm firmware needs to be rebuilt to create a custom prog_firehose_ddr.elf to support programming the eMMC at HS200 speeds. Third, the Qualcomm firmware needs to be rebuilt to support the bootloader booting from eMMC at HS200 speeds. If you have any questions on this please post in the forums.
Instructions for booting from eMMC will be provided once updated hardware makes this a less arduous process.
Go to top

